Table of Contents » Chapter 1 : Preliminaries : About Python
About Python 
Overview
The Python programming language is a versatile and general-purpose language that caters to various disciplines, including web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, scientific computing, and more. Python's syntax is simple, readable, straightforward, intuitive, and English-like, making it an excellent choice for beginners. The design philosophy of the language emphasizes code readability, and its syntax allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code than might be used in languages such as C++ or Java.
Python is beginner-friendly and powerful enough to satisfy the needs of experienced programmers and researchers. This balance is one of the key reasons behind its widespread popularity (See Figure 1). It boasts an extensive and active user community, which plays a vital role in the continuous development and improvement of the language. This vibrant community contributes to a vast ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, and tools, making Python highly extensible and versatile. Libraries like NumPy and pandas for data analysis, Django and Flask for web development, TensorFlow and PyTorch for machine learning, and Matplotlib and Seaborn for data visualization are just a few examples of Python's diverse capabilities.
Moreover, Python's compatibility and integration with other technologies and platforms further enhance its applicability in various domains, such as server-side web development, software development, mathematics, system scripting, etc. Python's platform independence ensures that Python applications can run on nearly any operating system with minimal modifications.
Python is a favorite language used in education due to its straightforward syntax and the breadth of its application. It is also heavily utilized in scientific research, data science, and machine learning for its robust data handling and analytical capabilities.
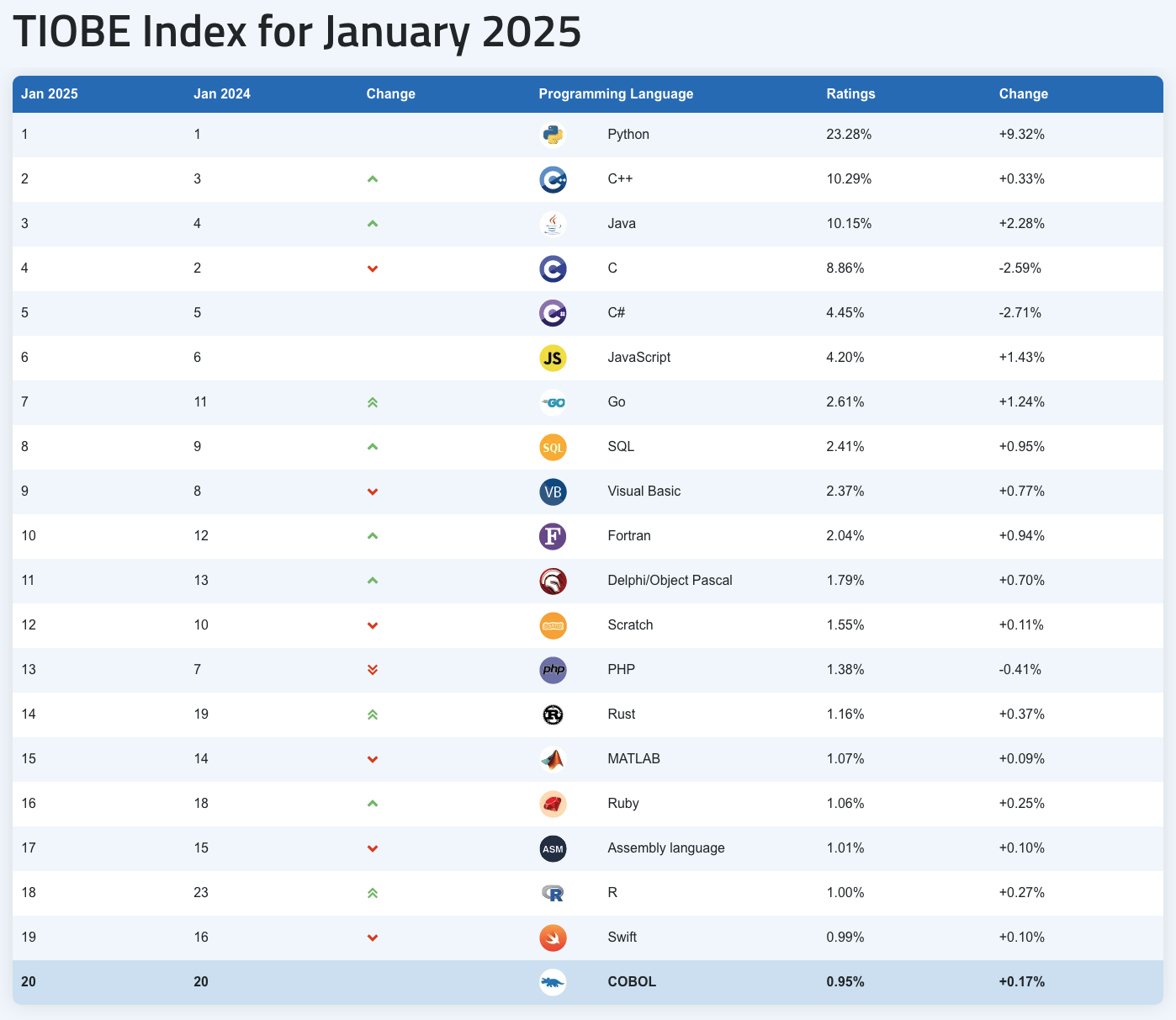
Figure 1: Python's Position on the Tiobe Index ↗ January 2025
History
The development of Python began in 1989 by its creator, Dutch software developer Guido van Rossum. The language was first released in 1991 and has steadily evolved since. Van Rossum's design goals included code readability, brevity, and language learning ease. He named the language Python after the film Monty Python. Today, Python is open-source and maintained by the Python Software Foundation (PSF).
Python's evolution has brought about the wide adoption of the language for development in many different contexts, such as web development, data analysis, data visualization, machine learning, artificial intelligence, scientific and mathematical computing, game development, robotics, web scraping, business applications, education, image processing, audio and video applications, natural language processing, and many others.
You can find the official documentation of the most recent version of Python at https://docs.python.org. The official documentation is always the best source of accurate information about the language. Also, that site maintains a historical documentation set for Python versions before to the most recent. Why is this important? If you are starting a new project in Python, conventional wisdom would suggest using the most current version, however, if you need to work on the code of an existing application written in an earlier version of Python. In that case, it will be important for you to be aware of the version it was originally developed in and you will likely have to work in that version of Python. There could be many reasons why upgrading existing applications to the latest version of Python may not be possible. On the other hand, you may find compelling reasons to move that application up into a more recent version - this is particularly true if that application was developed in a version previous to version 3.0.


