Programming Basics
Basic Operators
Operators in programming are symbols that we use to perform various mathematical or other actions between variables and values. Python supports a large number of operators that are used in many different scenarios. It would be difficult to try to memorize all of them at one time. So instead, we will take a look at some now, work with them, and then add more along the way as we learn more about Python.
The first operators we'll study are those used for simple mathematics. Most of these operators are used for math concepts you should be familiar with, such as addition, subtraction, etc. I'll provide a list of the arithmetic operators and then we'll look at how to use them in Python.
| Operator | Operation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition |
Adds two values together. Examples: |
| - | Subtraction |
Subtracts one value from another value. Examples: |
| * | Multiplication |
Multiples two values together. Examples: |
| / | Division |
Divides one value by another value. Be careful not to attempt to divide by zero. Examples: |
| % | Modulus |
Returns the remainder of dividing one value by another value. Examples: |
| ** | Exponentiation |
Raises the power of one value by another value. Examples: |
| // | Floor Division |
Divides one value by another value, then returns the floor value of the result. The floor value is the greatest integer less than or equal to the resulting value. Examples: |
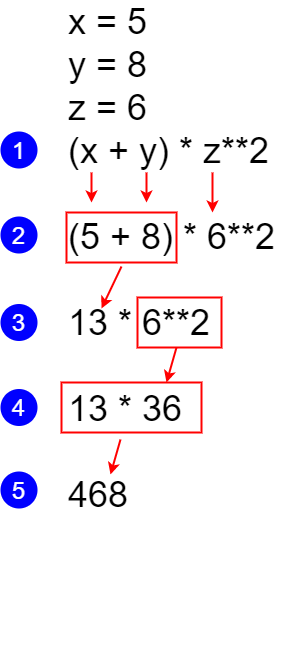
Precedence in mathematics means that when we have a mathematical expression with more than one operator, there is an established precedent that instructs us in what order to perform the calculation. Starting with the arithmetic operators, here is the order of precedence that is followed by Python:
Given the precedence rules above, we can combine arithmetic operators to create formulas and complex expressions as needed. For example, we could write the following:
x = 5
y = 8
z = 6
answer = (x + y) * z**2
print(answer)
|
|