Home » Chapter 1 : Preliminaries
Programming Tools & Computer Setup
In order to write code, in any programming language, we need access to software often referred to as programming tools. When we have the appropriate tools set up, we call that set of tools our development environment.
For our purposes, we will begin using a simple development environment called Google CoLaboratory (CoLab). We'll start there because CoLab requires no setup and is an easy place to begin to learn to write Python code. Later we will explore other types of develoment environments.
Google CoLaboratory (a.k.a. CoLab) is a free, cloud-based service offered by Google. It allows you to write and execute Python code in a web browser with no setup required. The only requirement to use CoLab is that you have a Google account (which is also free). Follow the steps below to get started with Google CoLaboratory:
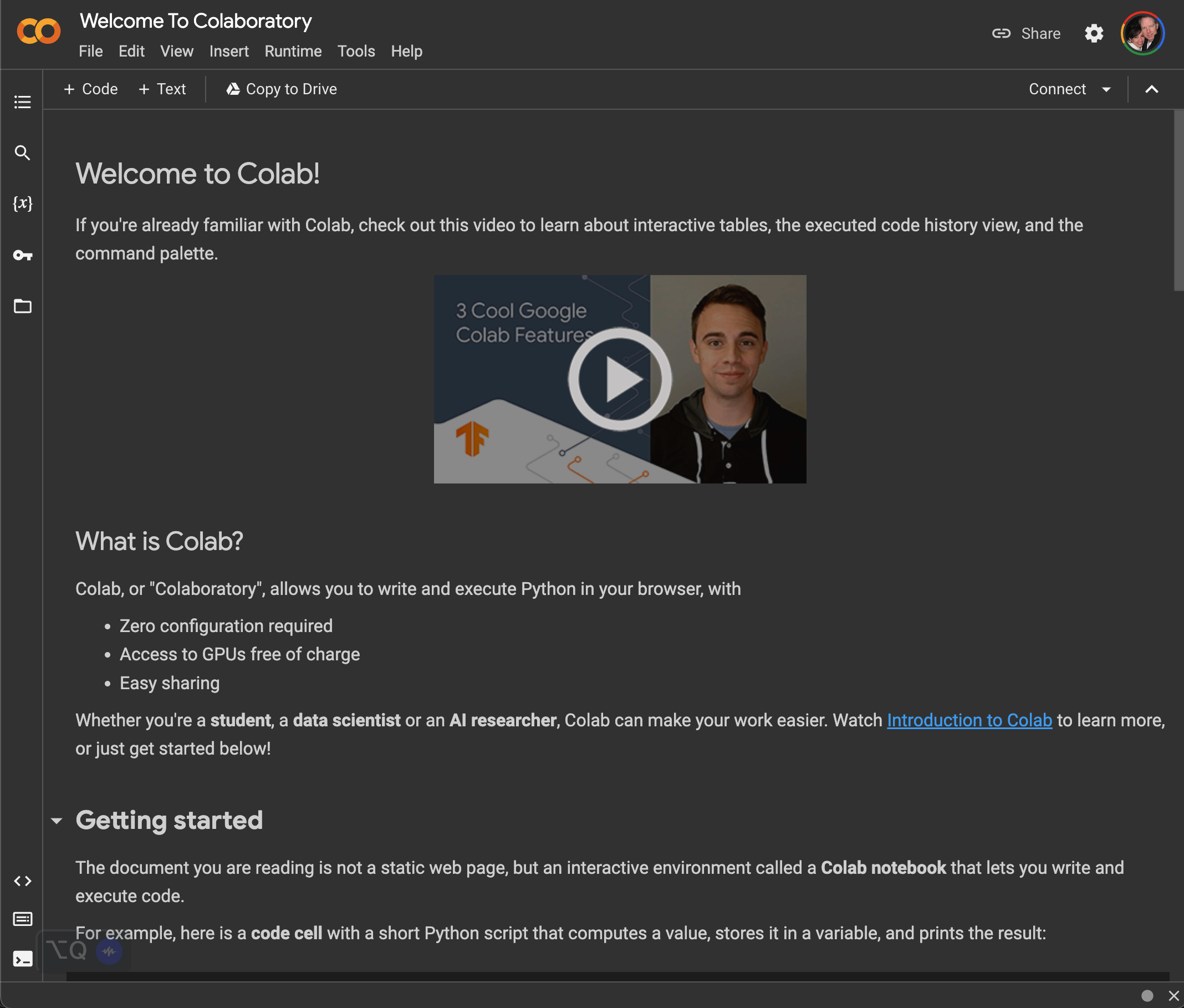

Note: Your pages might look a bit different, for example, I have dark mode set on my computer. If yours is not set that way, the CoLab pages will likely have white backrounds.
Now that you are signed-in to Google and connected to CoLab, follow the steps below to test your setup.
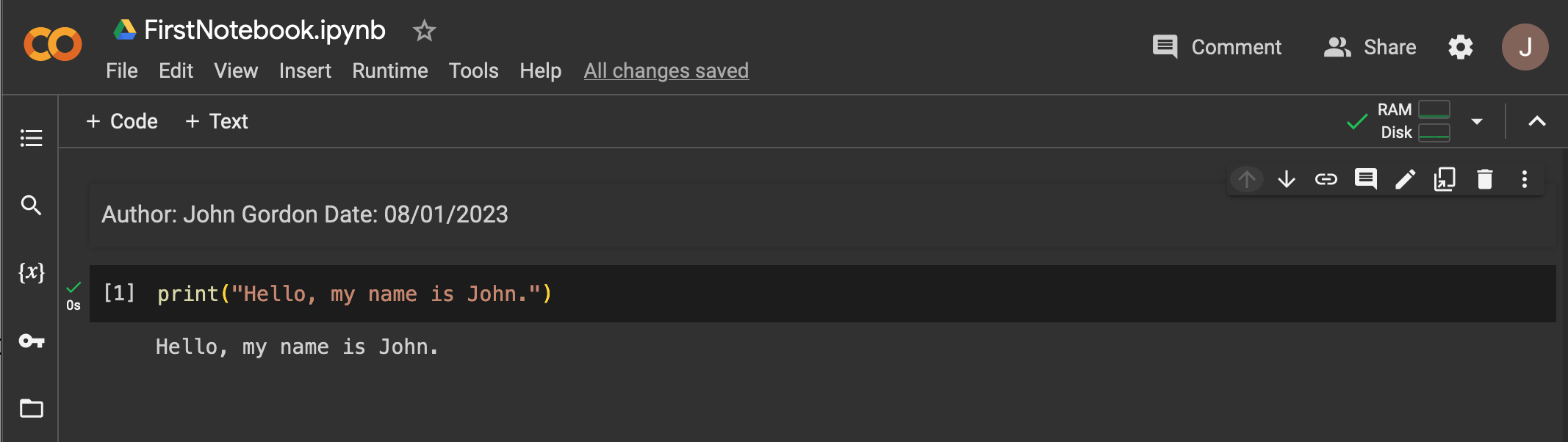
Follow the steps below to test your Google CoLab setup:

print("Hello, my name is John.")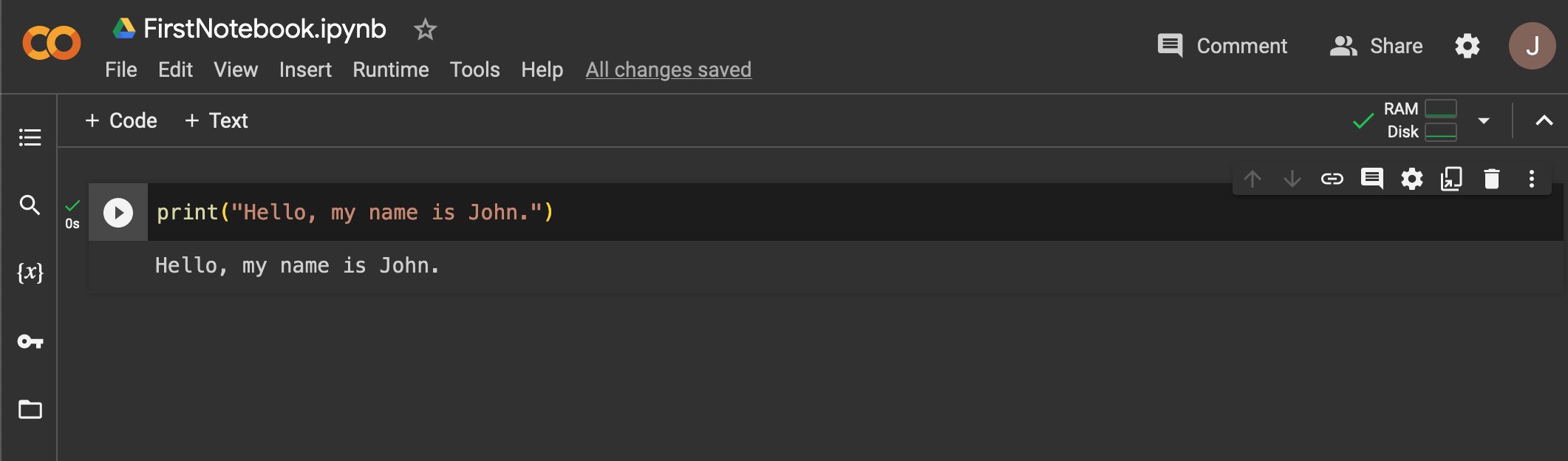


OpenAI ChatGPT is an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based chatbot that we will use as one of our programming toolset to learn how to make use of modern AI tools while still learning to code to a level of proficiency.
Follow the steps below to get started with OpenAI ChatGPT.
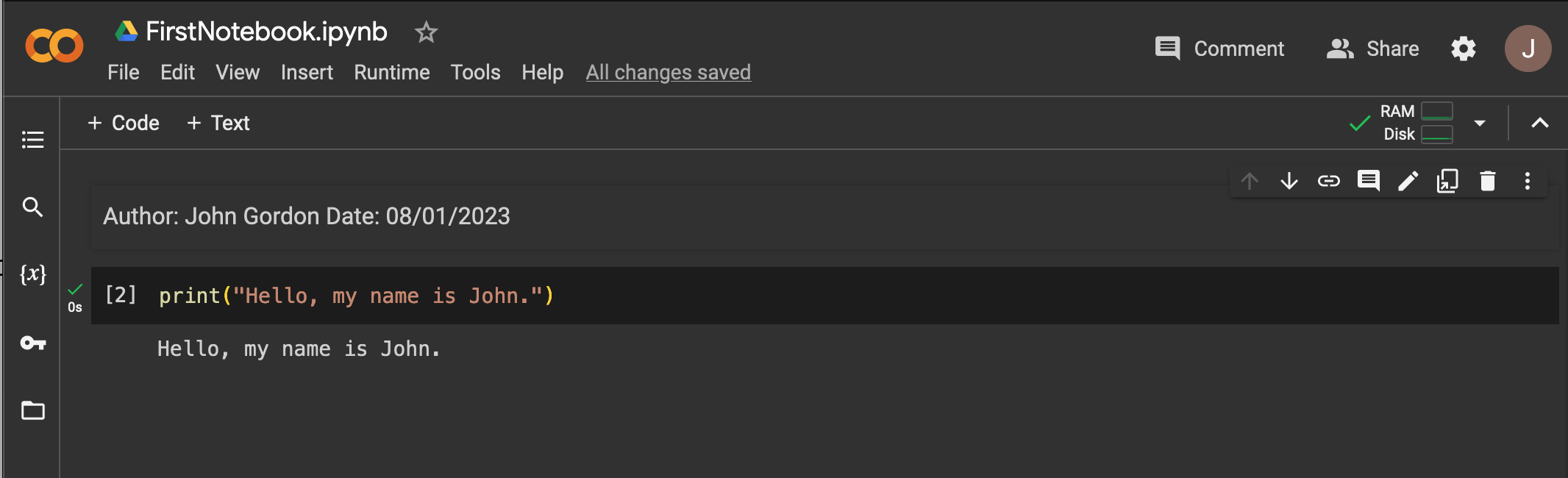
Follow the steps below to test your OpenAI ChatGPT setup:


print("Hello, my name is John.")




